
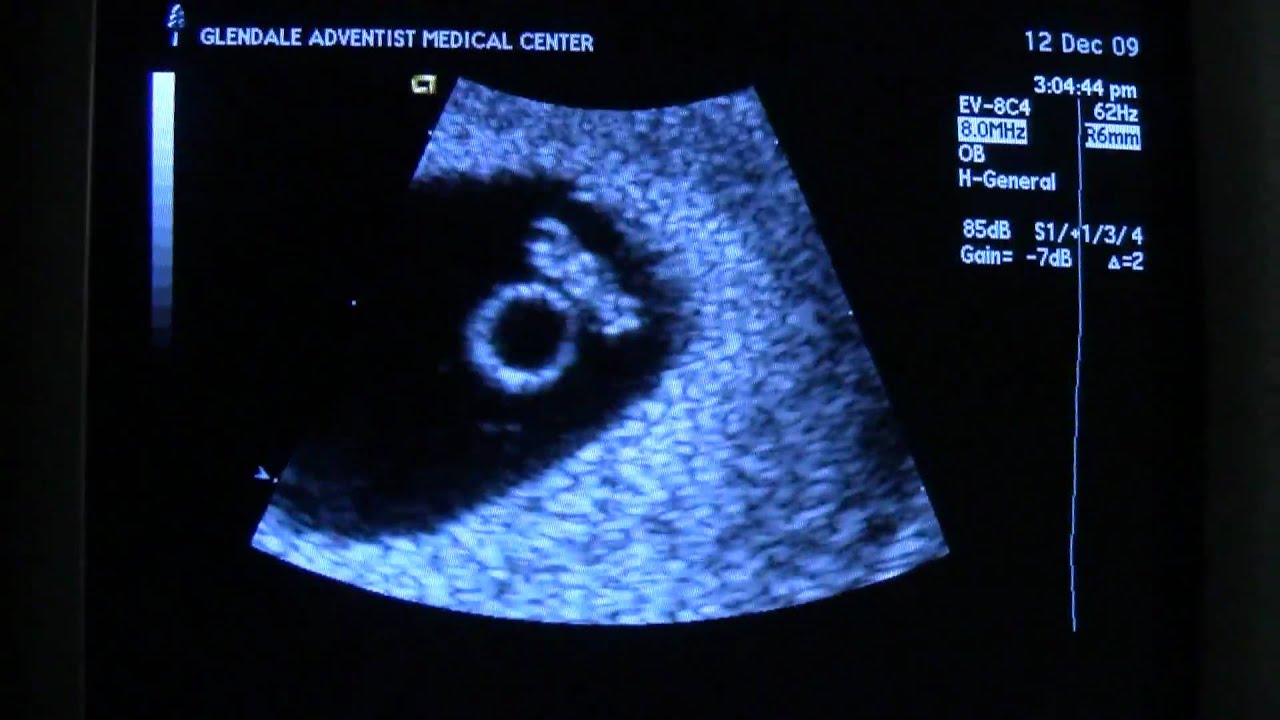
Chances are, if we listened more frequently during a woman’s pregnancy, we’d detect arrhythmias in more than the 1 to 2 percent we expect today. In less than 1 percent of infants, a fetal ectopic rhythm can trigger an abnormally high fetal heart rate, which puts the baby at risk for more serious cardiovascular issues.įetal heart arrhythmias are likely more common than we think. Once we determine the cause of the fetal arrhythmia, we will listen to your baby’s heart rhythm using a Doppler weekly until we’re confident the arrhythmia has resolved or will not affect the baby’s health.
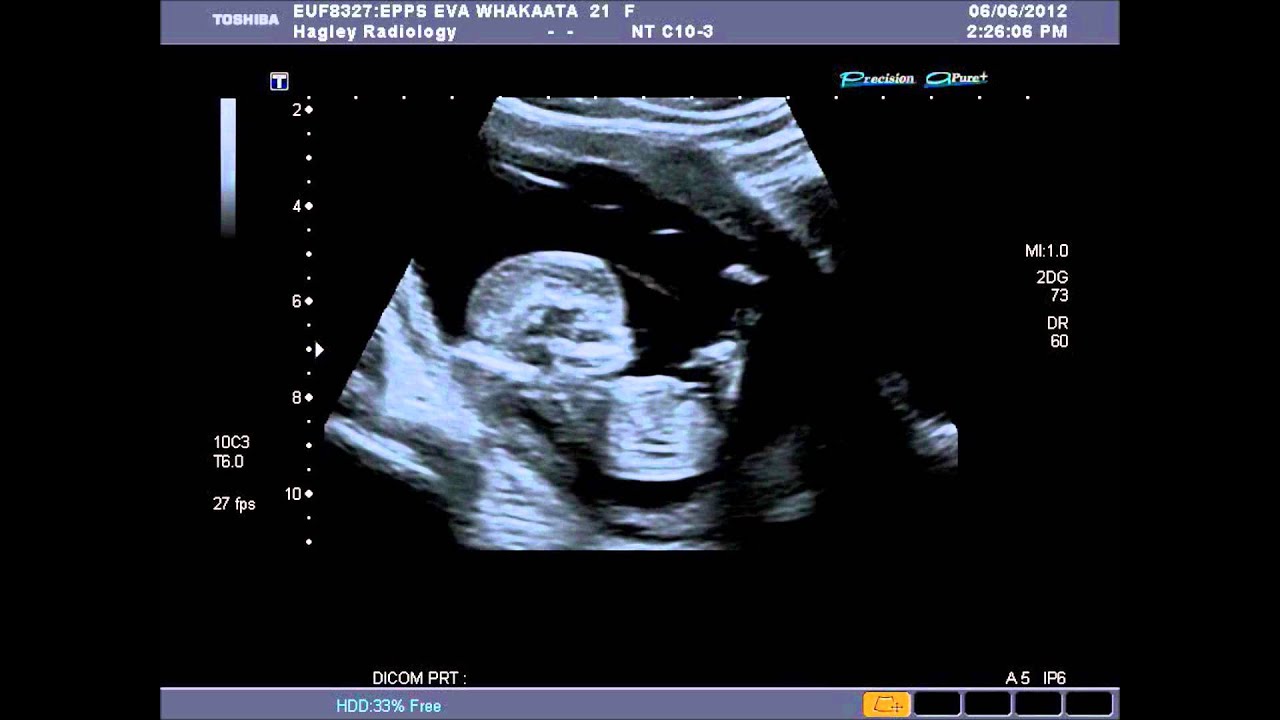
Caffeine: The MFM will discuss with you how much coffee, soda, and tea you consume daily and will recommend eliminating caffeine from your diet.But frequently, we find a logical explanation for the irregular rhythm that can be corrected with simple lifestyle changes.Ĭertain substances can contribute to irregular fetal heart beats. Understandably, many expecting parents feel anxious about this test. If the Ob/Gyn hears an abnormal rhythm, he or she will refer you to a maternal-fetal medicine doctor (MFM) or a pediatric cardiologist to evaluate the baby’s heart structure. I had a 6 week ultrasound and the babys heart rate came in at around 112 beats per minute. Ectopic rhythm: The heart produces early beats, which sound like extra or dropped beats.Tachyarrhythmia: The heart rate is too fast.Embryos with heart rates below 85 beats/ min during 6-8 weeks' gestation did not survive. A highly significant (p < 0.01) linear decrease was seen in fetal losses with increasing gestational age. Bradyarrhythmia: The heart rate is too slow. In groups 3 and 4, a heart rate of 146 beats/min or more was associated with the fewest losses (5.5 and 3.3, respectively).There are three types of fetal arrhythmias: Instead of hearing a “thump-THUMP-thump-THUMP” rhythm, the doctor might hear “thump … THUMP-THUMP … thump.” Detection of some dropped or extra beats (arrhythmia) is fairly common, occurring in 1 to 2 percent of pregnancies. The normal rate is 110 to 160 beats per minute, although it can be higher in the first trimester or during periods of fetal activity.īut the doctor also listens for proper heart rhythm, or a normal, steady balance of beats and rests between them. The doctor uses a Doppler ultrasound to gauge the fetal heart rate (the number of times the baby’s heart beats per minute) and makes sure it falls within the correct range.

And hearing it at every prenatal visit is comforting. doi:10.1148/radiology.Hearing a developing baby’s heartbeat is one of the milestones of pregnancy. Slow Embryonic Heart Rate in Early First Trimester: Indicator of Poor Pregnancy Outcome. Outcome of First-Trimester Pregnancies with Slow Embryonic Heart Rate at 6–7 Weeks Gestation and Normal Heart Rate by 8 Weeks at US.

FHR around 170 bpm may be classified as borderline fetal tachycardiaĪ rapid and irregular fetal heart rate is usually termed a fetal tachyarrhythmia.Related pathologyĪ slow fetal heart rate is termed fetal bradycardia and is usually defined as 1: This is followed by a decrease in FHR becoming on average:Īlthough in the healthy fetus the heart rate is usually regular, a beat-to-beat variation of approximately 5 to 15 beats per minute can be allowed. The FHR is then usually around 100 to 120 beats per minute (bpm).įHR then increases progressively over the subsequent 2-3 weeks becoming 7: Evolution through gestationĪlthough the myocardium begins to contract rhythmically by 3 weeks after conception (from spontaneously depolarizing myocardial pacemaker cells in the embryonic heart) it is first visible on sonography around 6 weeks of gestation. It is measurable sonographically from around 6 weeks and the normal range varies during gestation, increasing to around 170 bpm at 10 weeks and decreasing from then to around 130 bpm at term. A normal fetal heart rate (FHR) usually ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute (bpm) in the in utero period.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
